Mass Movement
Definition
Facts and figures
Further information
UN-SPIDER Regional Support Offices with hazard-specific expertise
Related content on the Knowledge Portal
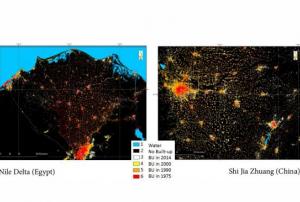
The Global Human Settlement (GHS) framework produces global open source spatial information about the human presence on the planet over time. This is in the form of built up maps, population density maps and settlement maps. This information is generated with evidence-based analytics and knowledge using new spatial data mining technologies. The framework uses heterogeneous data including global archives of fine-scale satellite imagery, census data, and volunteered geographic information. The data is processed fully automatically and generates analytics and knowledge reporting objectively and systematically about the presence of population and built-up infrastructures.
The guidelines will be reviewed and updated periodically, in order to integrate new best practices and to be responsive to evolutions in technology and end-user needs. The IWG-SEM chair has the responsibility to initiate the review, by agreement of the Working Group.
The production and the maintenance of the guidelines are based on a joint effort by the members of the International Working Group on Satellite-based Emergency Mapping (IWG- SEM), a voluntary group of organizations involved in satellite-based emergency mapping. It was founded to improve cooperation, communication and professional standards among the global network of satellite-based emergency mapping providers. The chairperson of the group is nominated for a term of one year and is responsible for organizing the monthly telecons and bi-annual meetings. The current chair is from the Department of Geoinformatics, Z_GIS University of Salzburg / Spatial Services Ltd, Austria…
Publishing institution:Intensive capacity development sessions for Pacific island countries (Cook Islands, Fiji, Kiribati, Micronesia (the Federated States of), Samoa, Solomon Islands, Tonga, and Vanuatu).
The project aims to enhance institutional and technical capacity for using geospatial data and technology applications and promote regional cooperation for sharing geospatial data for disaster management in Pacific island countries.
Publishing institution:Developed for the needs of the ASEAN sub-region in Asia and the Pacific, the handbooks can also be adapted for use in other regions.
The handbooks have been developed through expert working groups, in collaboration with United Nations partners including UNOOSA/UN-SPIDER, UNITAR-UNOSAT, and OCHA. As well as extensive consultation with space agencies, national disaster management authorities and regional institutions, including GISTDA, LAPAN, ASEAN Coordinating Centre for Humanitarian Assistance on Disaster Management and Asian Institute of Technology.
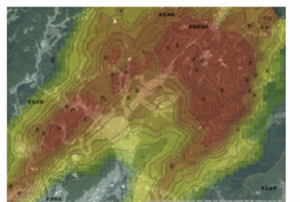
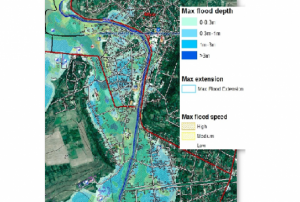
Publishing institution:Many of the sediment disasters were likely generated by the heavy rain. Sediment danger is alerted to during heavy rainfalls (≥20 mm/h), or when the total rainfall exceeds 100 mm. The new system can analyse the amount of accumulated rainfall, which is important for landslide disaster prevention.
read morePublishing institution:For a comprehensive and objective analysis of the settlement patterns, the DLR additionally developed an approach to display the spatial networks between the mapped settlements. It enables the computation of various form and centrality measures to characterize settlement patterns, at different spatial units, ranging from global to local scale.
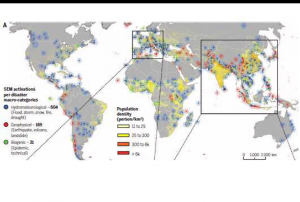
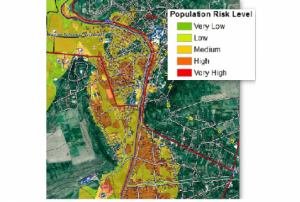
Publishing institution:CEMS is a core service of the European Union’s Earth Observation programme Copernicus. It supports all phases of the disaster management cycle by delivering warnings and risk assessments of floods and forest fires and by providing geospatial information derived from satellite images on the impact of natural and man-made disasters all over the world (before, during or after a crisis). The two Mapping services of CEMS (Rapid Mapping, Risk and Recovery Mapping) are delivering products since April 2012. The Risk & Recovery Mapping provided for example information for preparedness, disaster risk assessment and risk reduction related to earthquakes in Nepal, several post-disaster assessments for flood and fire events, reconstruction and recovery monitoring in Haiti, and multi-risk assessments for the Azores Islands in Portugal.
CEMS is coordinated by the European Commission (joint coordination between the Directorate Generals ECHO, JRC, GROW). Activation requests…
read morePublishing institution:- Publishing institution: