United
Nations
Office for Outer Space Affairs
UN-SPIDER Knowledge Portal

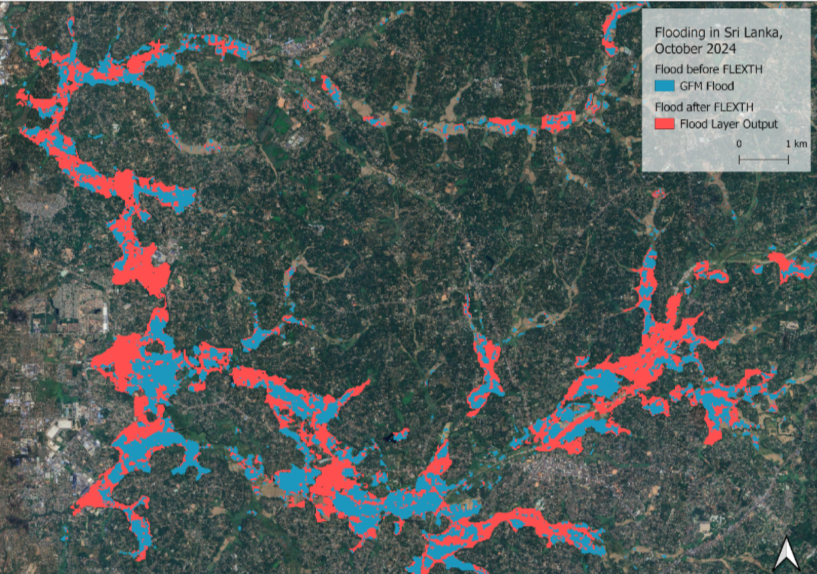
The objective of this practice is to improve flood maps with DTMs. This is necessary, as Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) sensors are not sensible to flood water on every land surface / land use class equally. That is especially the case in urban and densely vegetated areas.
During this practice, flood delineations from GFM are used and improved. Furthermore, water depths are calculated for the flooded areas, which is valuable information for rapid response teams as well as for estimating economic loss. Water depth cannot be estimated by satellite-based flood mapping (Betterle and Salamon 2024).
In October 2024, many provinces of Sri Lanka have been experiencing heavy rainfall and strong winds, causing floods and severe weather-related incidents that resulted in casualties and damage (Sri Lanka: Floods - Oct 2024 | ReliefWeb, accessed: 22.11.2024).
Nepal, Sri Lanka and Bangladesh experience an increased flood risk and extend of the monsoon season from June to October, with heavier rainfall potentially disrupting agricultural activities and affecting infrastructure (OCHA, 19.11.2024).
This practice can be applied to flooding events globally. It requires little to no knowledge of GIS and Remote Sensing. A basic understanding of Python code and virtual environments in Python is helpful to the analysis but is no requirement.

Neither UN-SPIDER nor the Regional Support Offices (RSOs) or their partners take any responsibility for the correctness of outputs from this recommended practice or decisions derived as a consequence.